|
|
|
|
|
TSUKUBA, Japan, Oct 3, 2013 - (ACN Newswire) - More than a century after the identification of organisms that cause tuberculosis (TB), this disease remains a global public health challenge. According to World Health Organization estimates, there were 8.7 million new cases in 2011 and 1.4 million deaths. Most new cases occur in developing countries that lack the facilities and trained personnel required for early detection of TB.
 | | A Rapid, Paper-based Diagnostic Test for Tuberculosis |
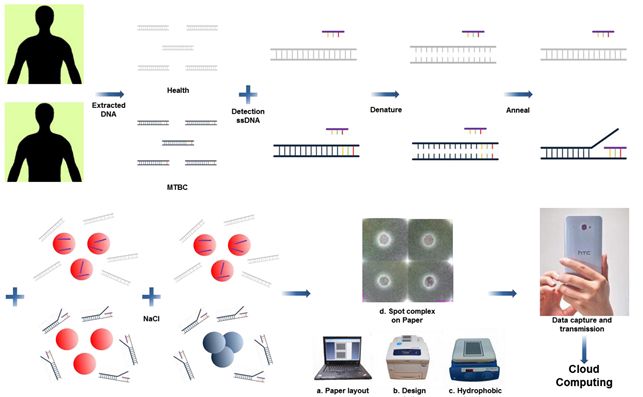
In a new study, published in the journal Science and Technology of Advanced Materials (STAM), researchers in Taiwan describe a simple, color-based diagnostic approach with the potential to detect target DNA sequences found in TB-causing mycobacteria - in just a fraction of the time required for established diagnostic tests.
The standard method for TB detection in a clinical setting involves culturing the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus, which requires 3-6 weeks to grow on solid culture media or 9-16 days in rapid liquid culture media. A faster alternative is the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology. However, it is still too slow (turnaround time 2-5 hours) and requires sophisticated infrastructure and trained personnel that might be unavailable in developing countries.
In their STAM paper, Tsung-Ting Tsai and colleagues employed gold nanoparticles and microfluidic paper-based analytical devices to achieve rapid diagnosis without the need for complex and time-consuming laboratory processes. They easily detected TB mycobacterium target sequences, and the turnaround time was approximately 1 hour after the human DNA was extracted from patients.
Although the authors are still optimizing their technology, they already believe that it will result in "affordable, sensitive, specific, user-friendly, rapid and robust, equipment-free, and highly end-user-deliverable diagnostic applications".
Related information:
[1] Tsung-Ting Tsai et al, Paper-based tuberculosis diagnostic devices with colorimetric gold nanoparticles, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 14 (2013) 044404
http://iopscience.iop.org/1468-6996/14/4/044404/
Media contacts:
National Institute for Materials Science, Tsukuba, Japan
Email: stam_office@nims.go.jp
Tel. +81-(0)29-859-2494
Topic: Research and development
Source: National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS)
Sectors: Science & Research, BioTech
https://www.acnnewswire.com
From the Asia Corporate News Network
Copyright © 2024 ACN Newswire. All rights reserved. A division of Asia Corporate News Network.
|
|
|