|
| Tuesday, 2 November 2021, 15:33 JST | |
| |  | |
Source: Denso | |
|
|
|
|
| Downsizing electrification products and improving vehicle fuel efficiency by using proprietary SiC technologies |
TOKYO, Nov 2, 2021 - (JCN Newswire) - DENSO Corporation has been contributing to spreading the use of electric vehicles, extending their mileage, and reducing CO2 emissions from vehicles by developing SiC (silicon carbide) power semiconductors, which incorporate DENSO's proprietary structures and processing technologies, and using them in its in-vehicle products.
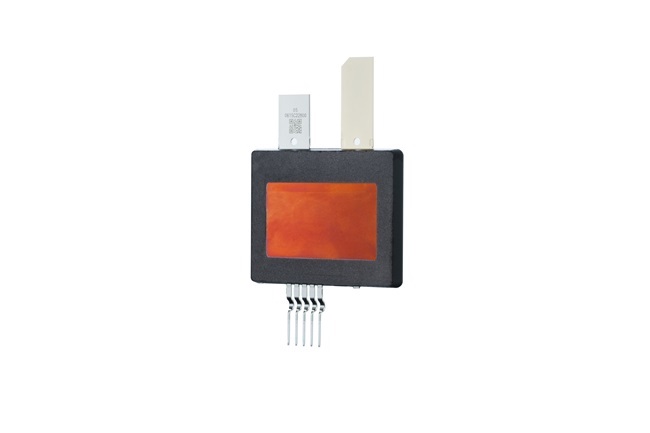 | | SiC power card |
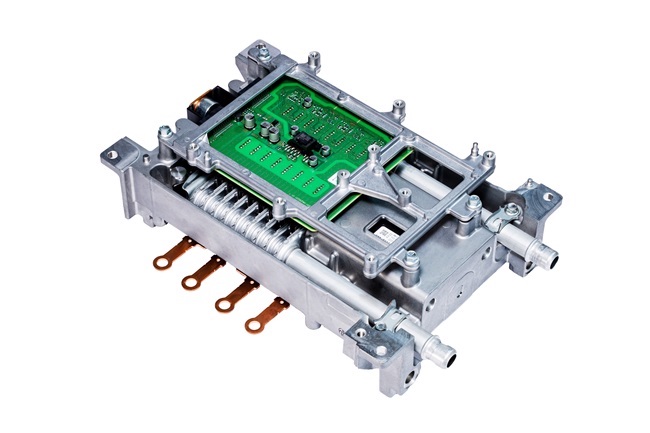 | | Booster power module |
 |
A power semiconductor is like the muscles in the human body. It moves components, such as inverters and motors (limbs), based on commands from an ECU (brain). Typical power semiconductors used in in-vehicle products are made from silicon (Si). In comparison, SiC offers superior performance in high-temperature, high-frequency, and high-voltage environments, and helps significantly reduce the power loss, size, and weight of inverters. Thus, SiC devices have attracted attention because they accelerate the electrification of vehicles.
For example, a booster power module, which incorporates DENSO's SiC power semiconductor, is about 30% smaller in volume with 70% less power loss than a conventional product with a Si power semiconductor. As a result, products have been made smaller and vehicle fuel efficiency improved.
DENSO calls these SiC technologies "REVOSIC," conveying the idea of making "changes" in society through innovative technologies. The company has been developing a comprehensive range of technologies from wafers to power modules, and will continue R&D on REVOSIC SiC technologies and spreading their use in electric vehicles to help realize a decarbonized society.
Introduction of developers
Tomoo Morino / R&D.Dept.4, Power Module Eng. Div.
I was in charge of determining the specifications of the SiC power semiconductor with the power module design department and designing the device structure based on the specifications. SiC has a low resistance compared to Si and so electric current can flow more easily. Due to this property, a prototype SiC device was damaged by a sudden surge of a large electric current. We collaborated with other departments to discuss how to prevent damage to devices in the market while taking full advantage of the low-loss performance of SiC, and the issue was solved with an idea which our department could not come up with alone: high-speed cut-off of the electric current using a special driver IC.
For now, few products are equipped with SiC, but as electric vehicles spread, we will increase the number of products with SiC and thus reduce CO2 emissions.
Tomohiro Mimura / R&D.Dept.4, Power Module Eng. Div.
I was in charge of the process design for manufacturing SiC power semiconductor devices. The hardness of SiC is second only to diamond, so it is more difficult to process than Si. I struggled to design a mass production process that can stably deal with microstructures of less than one micrometer.DENSO has been researching SiC for many years, and so there are many predecessors and senior employees. To solve this problem with SiC, I frequently talked with senior employees to learn from their experience and know-how, and also took full advantage of existing technologies. This made it possible to commercialize the product.
I hope to further improve the performance and quality of the device and reduce its cost so that SiC can be used in many more products.
Satoru Sugita / Design Dept. 2, Power Module Eng. Div.
I was in charge of the mounting design. I was responsible for determining the requirements to ensure reliability (e.g., materials, dimensions, processing conditions) required for installing SiC power semiconductors in power cards. In the design process, mounting defects occurred due to the high Young's modulus* (about triple that of Si), which is one of the characteristics of SiC materials. Such defects did not occur when Si was used. To cope with this unprecedented phenomenon, it was necessary to think laterally, beyond conventional ideas. To accurately understand the problem, I brought in an internal specialized department and external manufacturers of analysis instruments to gather different viewpoints and conducted genchi-genbutsu on-site verifications. This helped solve the problem and reflect the findings in the design requirements.
I hope to contribute to the use of electric vehicles and help create a decarbonized society by encouraging many customers to install SiC power semiconductor in various products.
*Young's modulus: A numerical value that represents the hardness of a material. It is also known as coefficient of elasticity.
Topic: Press release summary
Source: Denso
Sectors: Electronics
https://www.acnnewswire.com
From the Asia Corporate News Network
Copyright © 2026 ACN Newswire. All rights reserved. A division of Asia Corporate News Network.
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
| |
| Denso Related News |
|
| Tuesday, 3 February 2026, 19:36 JST |
| DENSO Announces Third Quarter Financial Results |
|
| Monday, 19 January 2026, 16:00 JST |
| DENSO to Promote Standardization of Automotive Software as an AUTOSAR Core Partner |
|
| Wednesday, 19 November 2025, 23:41 JST |
| DENSO and DELPHY Sign Joint Development Agreement to Accelerate Data-Driven Smart Horticulture |
|
| Thursday, 30 October 2025, 17:29 JST |
| DENSO Hosted a Press Briefing at JAPAN MOBILITY SHOW 2025 |
|
| Thursday, 16 October 2025, 22:53 JST |
| DENSO to Exhibit at JAPAN MOBILITY SHOW 2025 |
|
| More news >> |
|
|
|