TOKYO, Oct 9, 2024 - (JCN Newswire) - Fujitsu today announced that it is developing a system based on “Fujitsu Data Intelligence PaaS” (1) to realize a stable and efficient power supply for Kansai Transmission and Distribution, Inc. The system will be launched in March 2025.
As society confronts intensifying natural disasters, a declining labor population, and rising fuel costs, energy providers are facing challenges such as securing a stable supply of power in both regular and emergency situations, promoting the use of renewable energy, facility maintenance, and cost reduction.
This system, currently being developed by Fujitsu, will utilize “Fujitsu Data Intelligence PaaS” to collect, store, and visualize data from Kansai Transmission and Distribution and support a stable and efficient power supply, making it possible to quickly detect and investigate equipment errors. In addition to this system, Fujitsu is working to increase energy resilience by assessing power usage data to calculate the effect of avoiding planned power outages through the utilization of remote amperage control, as Kansai Transmission and Distribution moves toward the full-scale implementation of next-generation smart meters (2). By leveraging data, the system enables analysis to be carried out from various perspectives (i.e., staff, manager, senior executive, etc.) thereby improving operations and accelerating decision-making.
With this initiative, Fujitsu will support business transformation aimed at solving management issues using data and AI. In addition, Fujitsu plans to provide the electric power industry with new capabilities through its “Fujitsu Data Intelligence PaaS”, such as power demand forecasting and reduced-labor machine inspections using “Fujitsu Kozuchi”, its AI service from Mid-October 2024.
Fujitsu’s initiatives at Kansai Transmission and Distribution:Rapid error detection and increased efficiency through the visualization of power usage data and error information
In Japan, it has become increasingly common for private residences to generate their own electricity through solar power thanks in part to municipal government subsidies. At the same time, the number of skilled technicians is steadily decreasing year by year due to population aging. There is a heightened demand for energy companies to become more efficient in terms of how they inspect their business operations, including the operational status of equipment and power usage/generation measurements.
Kansai Transmission and Distribution used “Fujitsu Data Intelligence PaaS” to collect data on power usage (30-minute increments) from electricity smart meters and linked and visualized equipment and construction work data with error data. This has made it possible for the company to efficiently detect signs of equipment failure using this linked information, instead of the conventional practice of receiving error detection, checking the details against multiple systems, and then dispatching staff to the site if necessary. Furthermore, by applying the results of field assignments to the “Fujitsu Data Intelligence PaaS” and collecting data, seeing and analyzing error trends becomes possible, and error extraction accuracy can be continuously improved. This system is based on a pilot developed by Fujitsu in June 2024 and the company is planning to deploy it for operation by March 2025.
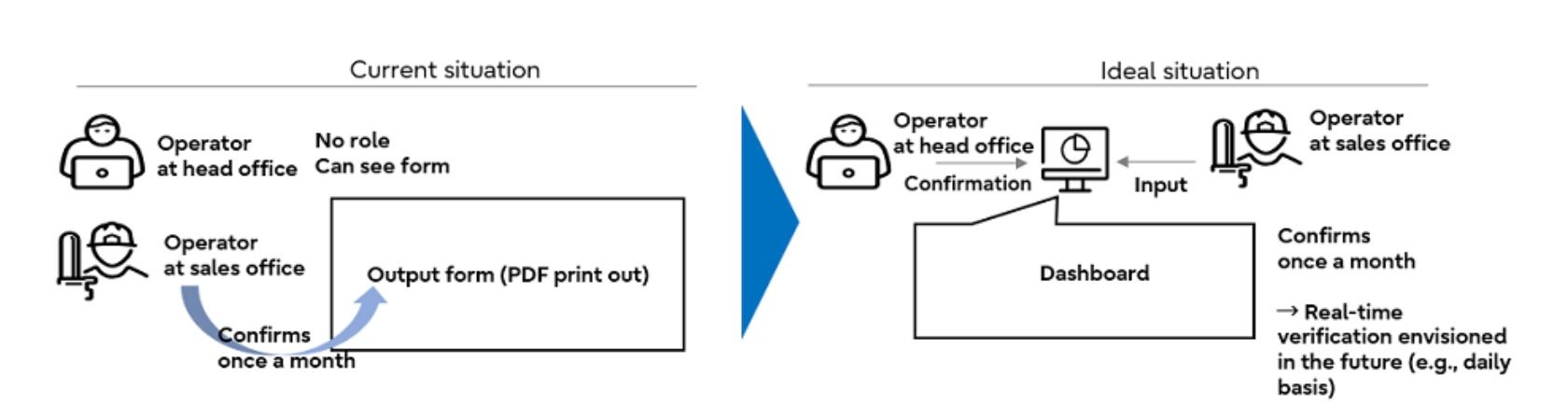
Figure 1: Diagram of the current vs. ideal situation of error detection services
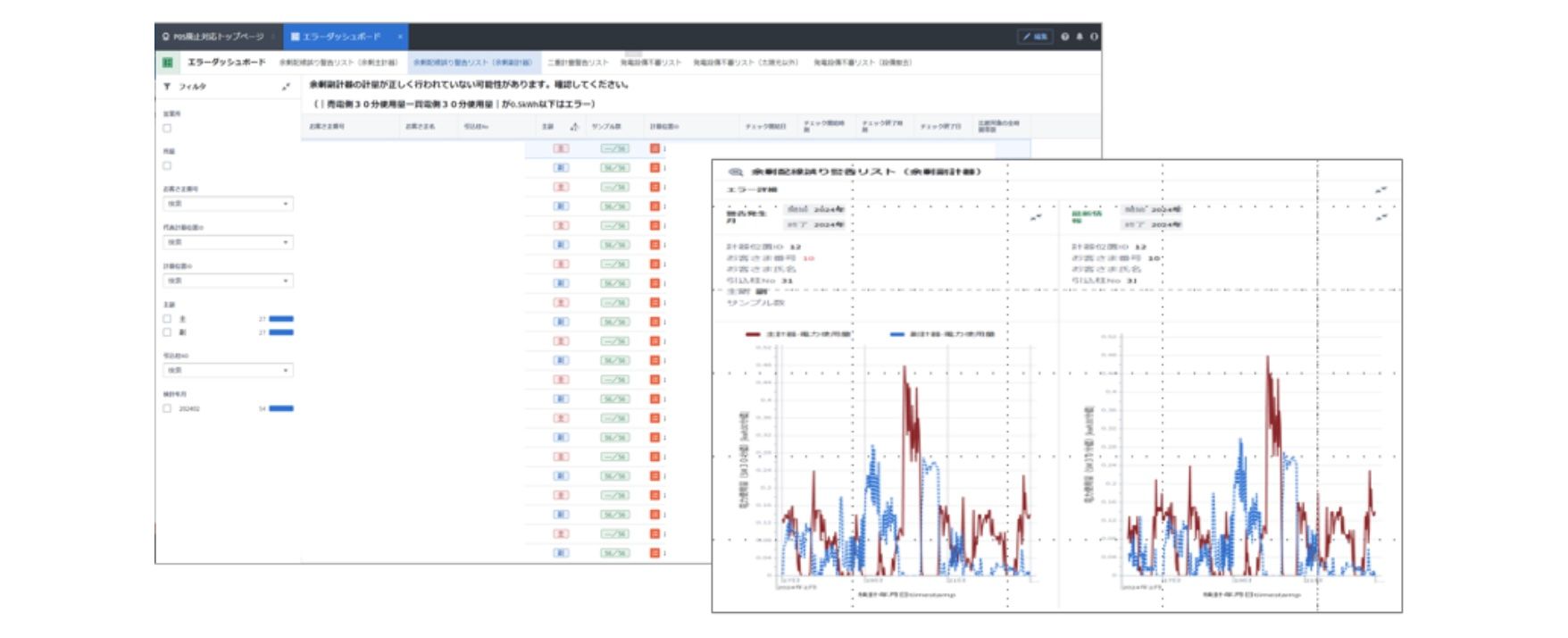
Figure 2: Error detection dashboard screen (3)
Verifying the effectiveness of the amperage control capabilities of next-generation smart meters
Fujitsu verified the effectiveness of the remote amperage control capabilities of next-generation smart meters to achieve a stable and efficient power supply. Remote amperage control is expected to play a role in plans to replace planned power outages that are currently employed as a last resort when the balance between the supply and demand of power is not expected to recover.According to estimates by Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) (4), avoiding planned power outages is expected to result in an economic benefit of approximately 135-150 billion yen over a ten-year period. The scheme requires the cooperation of consumers as they will need to reduce their power consumption to within the upper limit set on the remote amperage control unit in order to receive a steady power supply. To achieve this, energy providers, including Kansai Transmission and Distribution, must assess the impact that this initiative will have on users and calculate the optimal control values based on the amount of power that their supply capabilities will fall short by.
In this verification, Fujitsu utilized “Fujitsu Data Intelligence PaaS” and developed a prototype application able to visualize the effects of reducing energy consumption while varying the adoption rate of next-generation smart meters and the upper limit amperage control values. This application is based on electricity usage data (30-minute increments) obtained from approximately 13 million smart meters already in use. Through this, Fujitsu was able to confirm the impact of the controls on whole areas at specific times of day more effectively, and ascertain specific time blocks where consumers will need to reduce their energy consumption and the impact of reductions. Securing data on actual seasonal patterns of electricity usage allowed for the targeted use of amperage control units which has the potential to reduce the impact of energy saving measures on the general public and clarify periods when other measures should be deployed, including those focused on companies and factories that use more electricity.
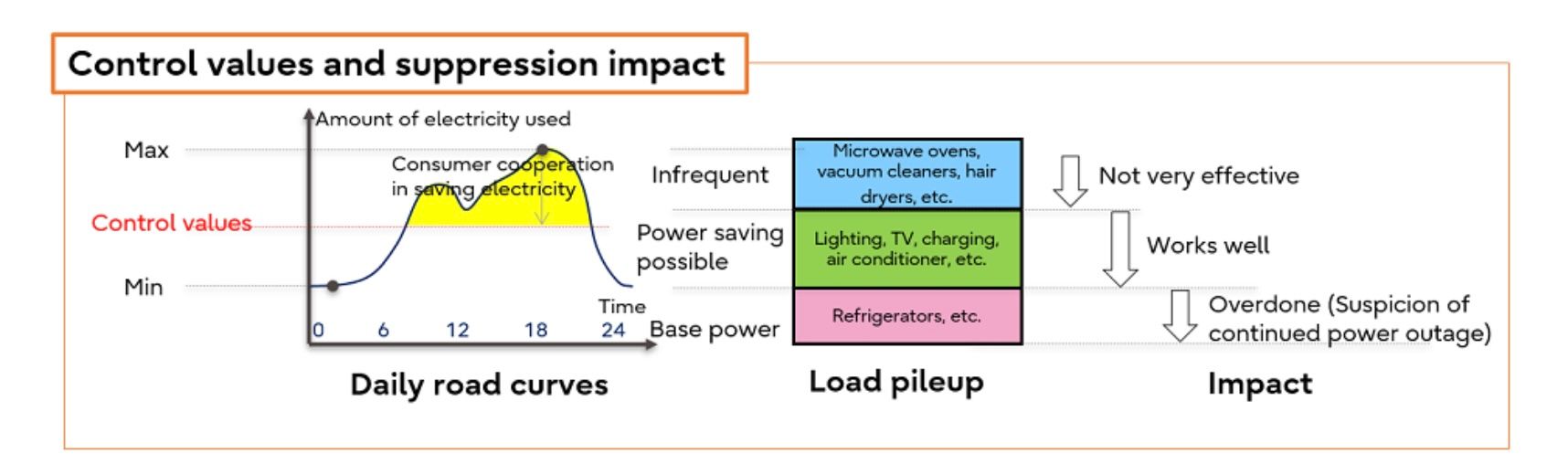
Figure 3: Diagram of control values and suppression impact
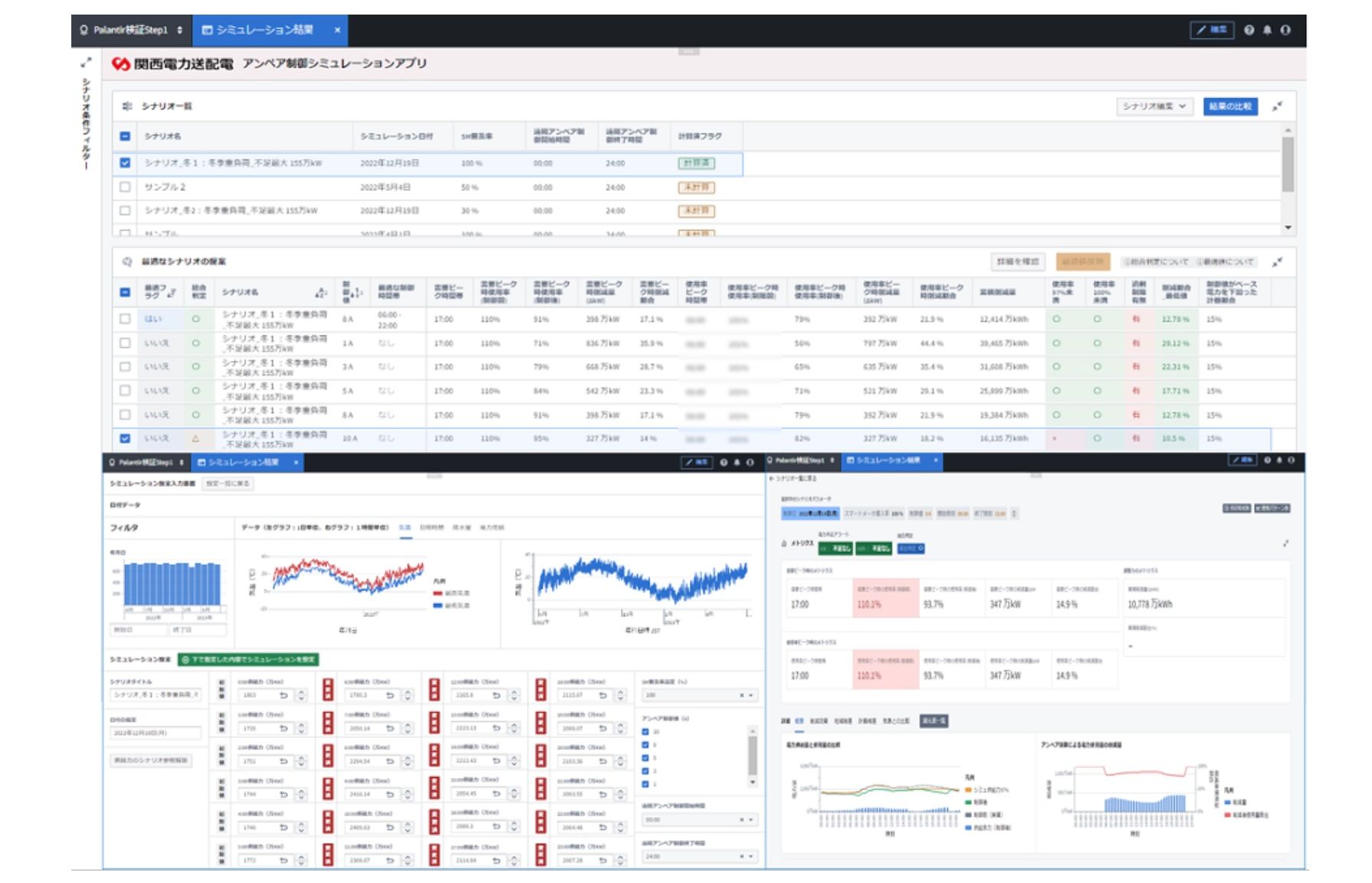
Figure 4: Remote amperage control simulation application screen
(1) “Fujitsu Data Intelligence PaaS” :Fujitsu’s platform that is made up of three components, “Fujitsu Kozuchi”, Fujitsu’s AI service, “Fujitsu Track and Trust”, blockchain technology that enables the collection and traceability of data across companies and industries, and data infrastructure, such as “Palantir Foundry” and “Microsoft Azure”.
(2) Next-generation smart meters :As the current electrical smart meters, which began to be used in 2014, start to reach the end of their operational lifespan, METI’s Agency for Natural Resources and Energy held a review committee for next-generation smart meter system from September 2020 to March 2022. In this review, experts and related parties in the industry studied the functions of the next-generation smart meters.
(3) Applications built on “Palantir Foundry”. © Palantir Technologies Inc.
(4) Estimates by METI: From the METI’s Agency for Natural Resources and Energy Review Committee’s summary of next-generation smart meter system review (published in May 2022).
About Fujitsu
Fujitsu’s purpose is to make the world more sustainable by building trust in society through innovation. As the digital transformation partner of choice for customers in over 100 countries, our 124,000 employees work to resolve some of the greatest challenges facing humanity. Our range of services and solutions draw on five key technologies: Computing, Networks, AI, Data & Security, and Converging Technologies, which we bring together to deliver sustainability transformation. Fujitsu Limited (TSE:6702) reported consolidated revenues of 3.7 trillion yen (US$26 billion) for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2024 and remains the top digital services company in Japan by market share. Find out more: www.fujitsu.com.
Press Contacts
Fujitsu Limited
Public and Investor Relations Division
Inquiries
Topic: Press release summary
Source: Fujitsu Ltd
Sectors: Enterprise IT
https://www.acnnewswire.com
From the Asia Corporate News Network
Copyright © 2026 ACN Newswire. All rights reserved. A division of Asia Corporate News Network.
|